Understanding GDPR and Its Impact on Blockchain Projects
- Introduction to GDPR and its importance in data protection
- Key principles of GDPR and how they apply to blockchain projects
- Challenges faced by blockchain projects in complying with GDPR regulations
- Strategies for blockchain projects to ensure GDPR compliance
- Impact of GDPR on the future of blockchain technology
- Case studies of blockchain projects navigating GDPR compliance
Introduction to GDPR and its importance in data protection
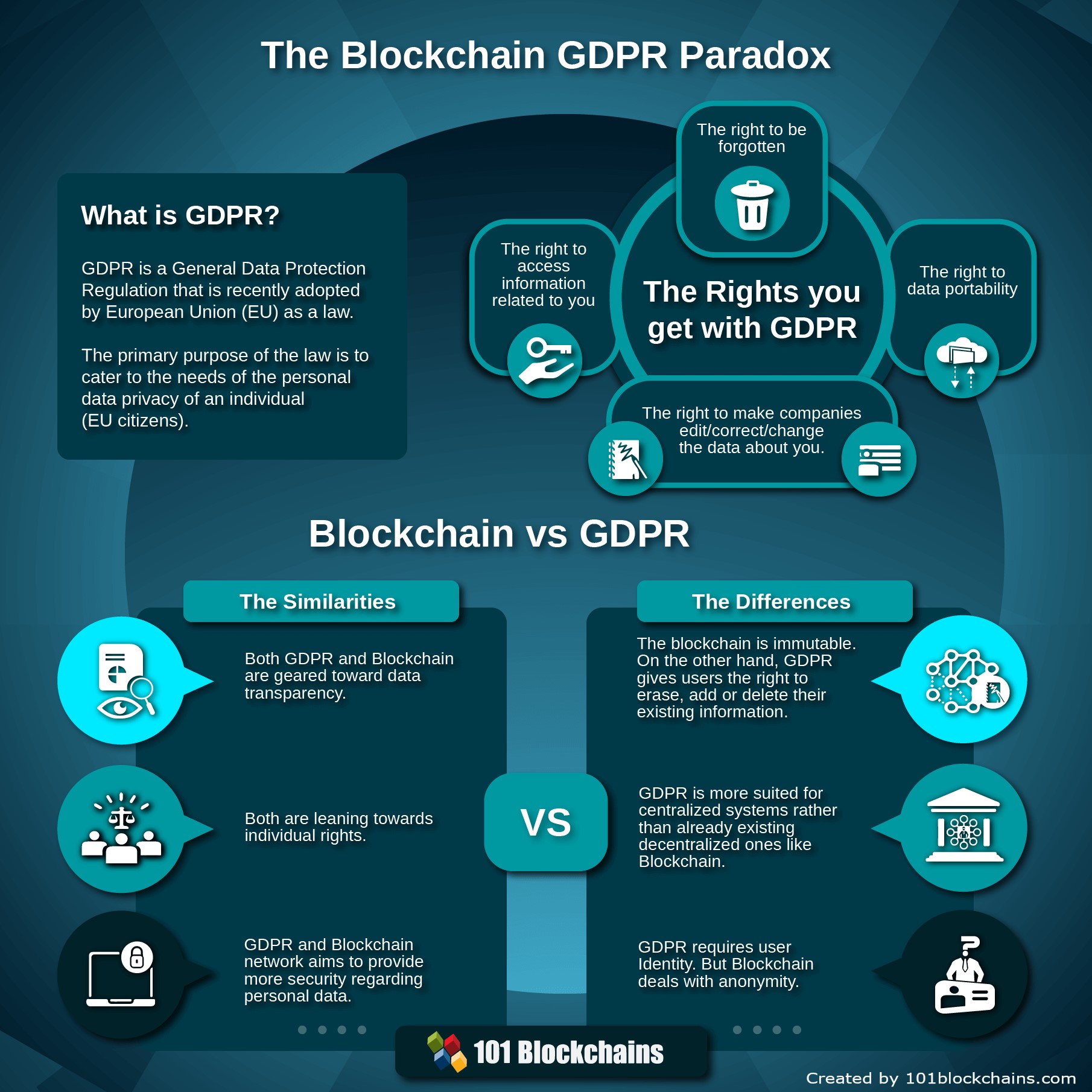
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a set of regulations designed to protect the personal data of individuals within the European Union (EU). It aims to give individuals more control over their personal data and ensure that companies handle this data responsibly. GDPR has had a significant impact on how businesses collect, store, and process data, including blockchain projects.
GDPR is essential for data protection as it helps prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, and misuse of personal information. By complying with GDPR, companies can build trust with their customers and avoid hefty fines for non-compliance. This regulation also promotes transparency and accountability in data processing practices, which is crucial in today’s digital age.
For blockchain projects, GDPR compliance is particularly important due to the decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain technology. While blockchain offers enhanced security and transparency, it also poses challenges in terms of data protection and privacy. Companies working on blockchain projects must ensure that they adhere to GDPR requirements to safeguard the personal data stored on the blockchain.
Overall, understanding GDPR and its importance in data protection is crucial for businesses, especially those involved in blockchain projects. By prioritizing data privacy and security, companies can not only comply with regulations but also build a strong foundation for trust and credibility in the digital landscape.
Key principles of GDPR and how they apply to blockchain projects
The key principles of General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are crucial for blockchain projects to understand and comply with. These principles apply to how personal data is collected, processed, stored, and shared within blockchain networks. Here are some key principles of GDPR and how they apply to blockchain projects:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Blockchain projects must ensure that the collection and processing of personal data are done lawfully, fairly, and transparently. Users should be informed about how their data is being used and have the ability to consent to its processing.
- Purpose limitation: Personal data collected within blockchain projects should only be used for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes. Any further processing of the data should be compatible with these purposes.
- Data minimization: Blockchain projects should only collect personal data that is necessary for the intended purpose. Unnecessary data should not be collected or stored within the blockchain network.
- Accuracy: It is essential for blockchain projects to ensure that personal data stored within the network is accurate and up to date. Measures should be in place to rectify any inaccuracies in a timely manner.
- Storage limitation: Personal data should not be kept within blockchain projects for longer than is necessary for the intended purpose. Data retention policies should be established to determine how long data will be stored.
- Integrity and confidentiality: Blockchain projects must implement appropriate security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, alteration, disclosure, or destruction. Encryption and access controls are essential for maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
- Accountability: Blockchain projects are responsible for demonstrating compliance with GDPR principles. This includes keeping records of data processing activities, conducting data protection impact assessments, and appointing a data protection officer if required.
Challenges faced by blockchain projects in complying with GDPR regulations
Blockchain projects face several challenges when it comes to complying with GDPR regulations. One of the main issues is the decentralized nature of blockchain technology, which makes it difficult to identify the data controller and data processor, as required by GDPR. This lack of clarity can lead to confusion and potential non-compliance.
Another challenge is the immutability of data on the blockchain. GDPR grants individuals the “right to be forgotten,” meaning they can request the deletion of their personal data. However, on a blockchain, once data is recorded, it cannot be easily erased. This presents a significant hurdle for blockchain projects in meeting GDPR requirements.
Additionally, the cross-border nature of blockchain projects can complicate GDPR compliance. Since the regulation applies to any organization processing data of EU residents, blockchain projects that operate internationally must navigate varying data protection laws and regulations in different jurisdictions.
Furthermore, the transparency and pseudonymous nature of blockchain technology can also pose challenges in complying with GDPR’s requirements for data minimization and purpose limitation. Ensuring that only necessary personal data is stored and processed, and that it is only used for the specified purposes, can be complex in a blockchain environment.
In conclusion, blockchain projects must carefully consider the unique challenges they face in complying with GDPR regulations. By addressing issues such as decentralized control, data immutability, cross-border operations, and data transparency, blockchain projects can work towards aligning their practices with GDPR requirements while leveraging the benefits of blockchain technology.
Strategies for blockchain projects to ensure GDPR compliance
When it comes to ensuring GDPR compliance for blockchain projects, there are several strategies that can be implemented to mitigate risks and protect user data. Here are some key approaches to consider:
- Transparency: Be transparent with users about how their data is being collected, stored, and used within the blockchain project. Provide clear and concise information about data processing activities.
- Data Minimization: Only collect and store the data that is necessary for the functioning of the blockchain project. Avoid collecting excessive or irrelevant information that could pose a risk to GDPR compliance.
- Security Measures: Implement robust security measures to protect user data from unauthorized access, breaches, or leaks. Utilize encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to ensure data protection.
- Consent Mechanisms: Obtain explicit consent from users before processing their personal data within the blockchain project. Allow users to easily withdraw their consent if they choose to do so.
- Data Subject Rights: Respect the rights of data subjects as outlined in the GDPR, such as the right to access, rectify, or erase their personal data. Establish procedures to handle data subject requests promptly and effectively.
By following these strategies, blockchain projects can align with GDPR requirements and build trust with users regarding data privacy and protection. It is essential to prioritize GDPR compliance to avoid potential legal consequences and reputational damage in the long run.
Impact of GDPR on the future of blockchain technology
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has had a significant impact on the future of blockchain technology. GDPR aims to protect the personal data of individuals within the European Union by regulating how organizations collect, store, and process this information. Blockchain projects must now comply with GDPR requirements to ensure the privacy and security of user data.
One of the key challenges that blockchain projects face in light of GDPR is the issue of data transparency. Blockchain technology is designed to be transparent and immutable, allowing for secure and decentralized data storage. However, GDPR requires that individuals have the right to access, correct, and delete their personal data. This presents a conflict between the principles of blockchain and the requirements of GDPR.
Another important consideration for blockchain projects is the concept of data minimization. GDPR mandates that organizations only collect and store personal data that is necessary for a specific purpose. This poses a challenge for blockchain projects that rely on the widespread sharing of data across a network. Developers must find ways to balance the need for data sharing with the requirements of GDPR.
Despite these challenges, GDPR has the potential to drive innovation in the blockchain space. By forcing developers to prioritize data privacy and security, GDPR can lead to the development of new solutions that enhance the protection of user data. Blockchain projects that successfully navigate the requirements of GDPR will be well-positioned to build trust with users and stakeholders, ultimately driving the adoption of blockchain technology in the future.
Case studies of blockchain projects navigating GDPR compliance
Several blockchain projects have successfully navigated the challenges of GDPR compliance by implementing innovative solutions. One such project is a supply chain management platform that utilizes blockchain technology to securely track and trace products throughout the supply chain. By leveraging blockchain’s immutable ledger, the platform ensures data integrity and transparency while also complying with GDPR regulations.
Another case study involves a healthcare data management system that uses blockchain to securely store and share patient records. By encrypting data and providing patients with control over their information, the system ensures GDPR compliance while also enhancing data security and privacy.
Furthermore, a financial services platform has integrated blockchain technology to streamline cross-border transactions while maintaining GDPR compliance. By implementing data protection measures such as pseudonymization and encryption, the platform ensures that personal data is handled in accordance with GDPR requirements.



