The Legal Status of Stablecoins and Central Bank Digital Currencies
- Understanding Stablecoins: A Legal Perspective
- The Rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies: Implications for the Financial System
- Regulatory Challenges Surrounding Stablecoins
- The Role of Central Banks in Regulating Digital Currencies
- Stablecoins vs Central Bank Digital Currencies: A Comparative Analysis
- Legal Frameworks for Issuing and Using Stablecoins and CBDCs
Understanding Stablecoins: A Legal Perspective
Stablecoins have gained significant attention in the financial world due to their potential to address volatility issues associated with traditional cryptocurrencies. From a legal perspective, it is crucial to understand the regulatory framework surrounding stablecoins to ensure compliance and mitigate risks.
One key aspect to consider is the classification of stablecoins under existing laws. Depending on their design and backing assets, stablecoins may fall under different regulatory categories such as securities, commodities, or e-money. This classification determines the legal requirements and obligations that issuers must adhere to.
Moreover, the issuance and circulation of stablecoins may raise concerns related to consumer protection, anti-money laundering (AML), and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations. Compliance with these regulations is essential to prevent illicit activities and safeguard the integrity of the financial system.
Central banks and financial authorities around the world are closely monitoring the development of stablecoins and considering the potential impact on monetary policy and financial stability. In response to the rise of stablecoins, some central banks are exploring the concept of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) as a way to maintain control over the monetary system.
Overall, understanding the legal implications of stablecoins is crucial for market participants to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape effectively. By staying informed and proactive in compliance efforts, stakeholders can contribute to the responsible growth of stablecoin markets while minimizing legal risks and ensuring investor protection.
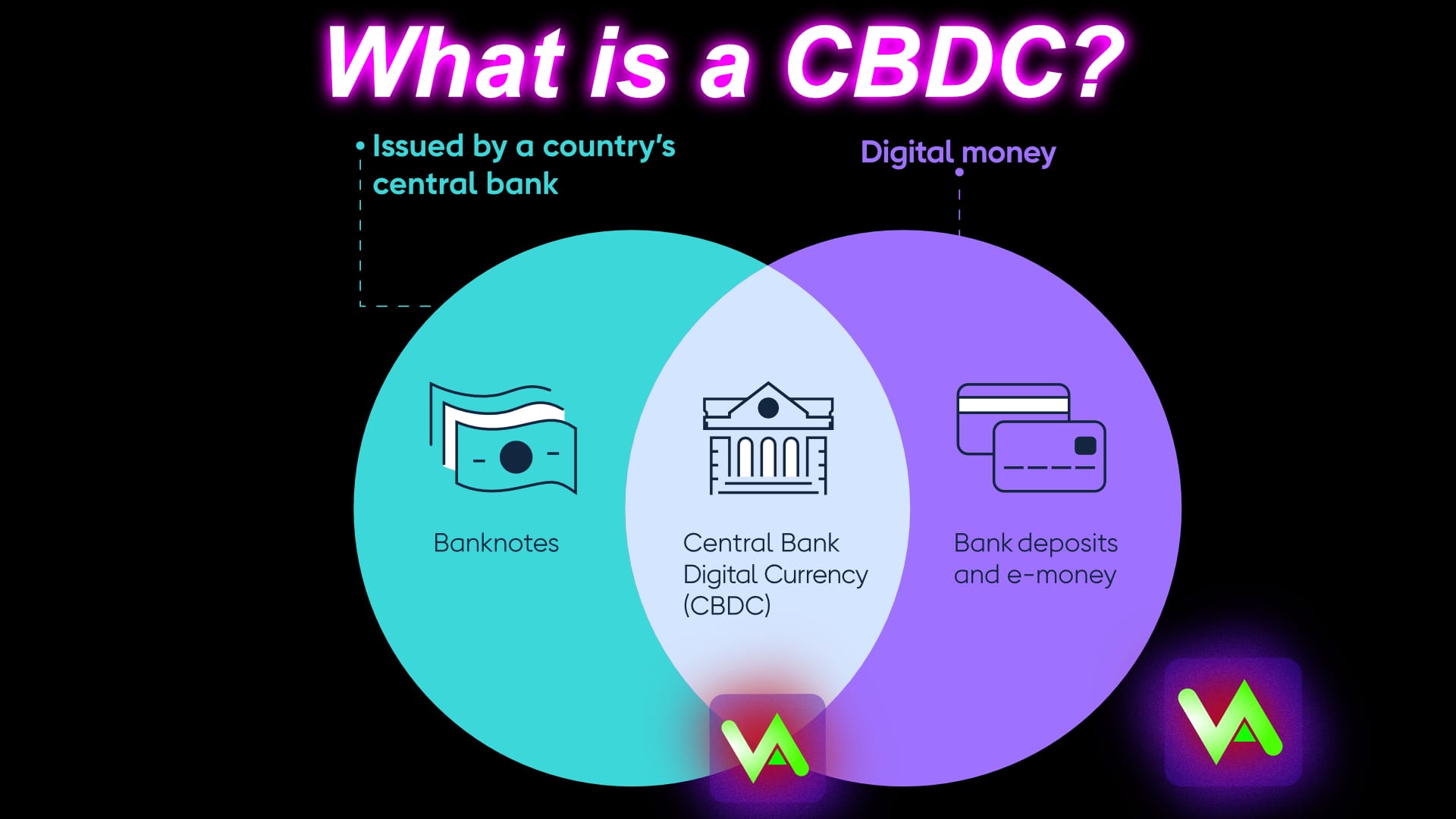
The Rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies: Implications for the Financial System
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) have been gaining momentum in recent years as central banks around the world explore the possibility of issuing their own digital currencies. The rise of CBDCs poses implications for the financial system, with potential impacts on monetary policy, financial stability, and the overall functioning of the economy.
One of the key implications of CBDCs is the potential to revolutionize the way we think about money and payments. By providing a digital alternative to physical cash, CBDCs could streamline transactions, reduce costs, and increase financial inclusion. Additionally, CBDCs could enable central banks to implement monetary policy more effectively by providing greater control over the money supply.
However, the introduction of CBDCs also raises concerns about privacy, security, and the role of commercial banks in the financial system. Critics argue that CBDCs could undermine the traditional banking model by allowing individuals and businesses to hold accounts directly with the central bank, bypassing commercial banks altogether. This could have far-reaching implications for the stability of the banking system and the transmission of monetary policy.
Regulatory Challenges Surrounding Stablecoins
Stablecoins present unique regulatory challenges that need to be addressed by policymakers and regulators. The main concerns revolve around issues such as consumer protection, financial stability, and anti-money laundering compliance.
One of the key challenges surrounding stablecoins is the potential impact on the traditional banking system. As stablecoins gain popularity and usage, they could pose a threat to the stability of the financial system, as they may not be subject to the same regulatory oversight as traditional banks.
Another area of concern is the potential for stablecoins to be used for illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. Regulators are working to ensure that stablecoin issuers have robust anti-money laundering and know-your-customer controls in place to prevent such activities.
Moreover, the lack of a clear regulatory framework for stablecoins creates uncertainty for both issuers and users. Without clear guidelines on how stablecoins should be regulated, there is a risk of regulatory arbitrage and inconsistent treatment across jurisdictions.
Overall, addressing the regulatory challenges surrounding stablecoins will require a coordinated effort from regulators, policymakers, and industry participants to ensure that stablecoins can coexist with existing financial systems in a safe and compliant manner.
The Role of Central Banks in Regulating Digital Currencies
Central banks play a crucial role in regulating digital currencies, including stablecoins and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). One of the primary responsibilities of central banks is to ensure the stability and integrity of the financial system. **Digital currencies** have the potential to disrupt traditional financial systems and can pose risks to financial stability if not properly regulated. Central banks have the authority to oversee and supervise digital currencies to mitigate these risks.
Central banks monitor the issuance and circulation of digital currencies to safeguard against potential threats such as money laundering, terrorism financing, and fraud. By setting regulatory frameworks and guidelines, central banks can enforce compliance standards for digital currency issuers and service providers. **Regulation** also helps to protect consumers and investors from scams and fraudulent activities in the digital currency market.
Moreover, central banks are responsible for maintaining price stability and controlling inflation. The introduction of CBDCs can impact the monetary policy of a country, as it provides central banks with more direct control over the money supply. By issuing and regulating CBDCs, central banks can influence interest rates, money supply, and economic growth. This level of control is essential for central banks to achieve their mandate of ensuring price stability and **economic growth**.
In conclusion, central banks play a crucial role in regulating digital currencies to safeguard financial stability, protect consumers, and maintain control over monetary policy. By establishing regulatory frameworks and overseeing the issuance of digital currencies, central banks can mitigate risks and ensure the integrity of the financial system. The evolution of digital currencies requires central banks to adapt and innovate their regulatory approaches to effectively address the challenges and opportunities presented by this rapidly changing **landscape**.
Stablecoins vs Central Bank Digital Currencies: A Comparative Analysis
When comparing **stablecoins** and **central bank digital currencies** (CBDCs), it is important to consider the key differences between the two types of digital currencies. **Stablecoins** are typically issued by private entities and are pegged to **fiat currencies** or other assets to maintain price stability. On the other hand, **CBDCs** are digital currencies issued by central banks and are considered legal tender.
One of the main distinctions between **stablecoins** and **CBDCs** is the entity responsible for issuing and regulating them. **Stablecoins** are issued by private companies, which means they are subject to less stringent regulatory oversight compared to **CBDCs**, which are issued and regulated by central banks. This key difference can have significant implications for the stability and security of the digital currency in question.
Another important factor to consider when comparing **stablecoins** and **CBDCs** is the level of decentralization. **Stablecoins** are typically centralized, meaning that they are controlled by a single entity or group of entities. In contrast, **CBDCs** are issued and controlled by central banks, which are typically government entities. This difference in decentralization can impact the trustworthiness and security of the digital currency.
Additionally, the purpose of **stablecoins** and **CBDCs** differs. **Stablecoins** are primarily used for transactions and as a store of value, while **CBDCs** are designed to complement or potentially replace physical cash. This distinction in purpose can influence the adoption and usage of the digital currency in question.
In conclusion, while **stablecoins** and **CBDCs** share some similarities as digital currencies, they also have key differences that set them apart. Understanding these variances is essential for policymakers, businesses, and consumers looking to navigate the evolving landscape of digital finance.
Legal Frameworks for Issuing and Using Stablecoins and CBDCs
The legal frameworks surrounding the issuance and utilization of stablecoins and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) play a crucial role in determining their legitimacy and acceptance in the financial world. These frameworks establish guidelines and regulations that govern how stablecoins and CBDCs can be created, distributed, and used within the market.
One key aspect of the legal framework for stablecoins and CBDCs is the requirement for issuers to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations. These regulations are put in place to prevent illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. By ensuring that issuers verify the identities of users and monitor transactions for suspicious activities, regulators can mitigate the risks associated with stablecoins and CBDCs.
Another important consideration within the legal framework is the need for stablecoin issuers to maintain sufficient reserves to back the value of the stablecoin. This requirement ensures that users can redeem their stablecoins at any time for the underlying asset, thus providing stability and trust in the stablecoin’s value. Additionally, regulations may also dictate how these reserves are managed and audited to ensure transparency and accountability.
In the case of CBDCs, the legal framework typically involves the central bank as the sole issuer and regulator of the digital currency. This centralized control allows the central bank to maintain monetary policy objectives and ensure the stability of the financial system. Regulations surrounding CBDCs may also address issues such as privacy, data security, and interoperability with existing payment systems.
Overall, the legal frameworks for issuing and using stablecoins and CBDCs are essential for establishing trust, stability, and regulatory compliance within the digital currency ecosystem. By adhering to these frameworks, issuers and users can navigate the evolving landscape of digital currencies while mitigating risks and promoting financial inclusion.



