How Smart Contracts are Transforming Legal Agreements
- Understanding the basics of smart contracts
- The benefits of using smart contracts in legal agreements
- Challenges and limitations of smart contracts in the legal industry
- Real-world examples of smart contracts revolutionizing legal processes
- Exploring the future of smart contracts in the legal sector
- Key considerations when implementing smart contracts in legal agreements
Understanding the basics of smart contracts
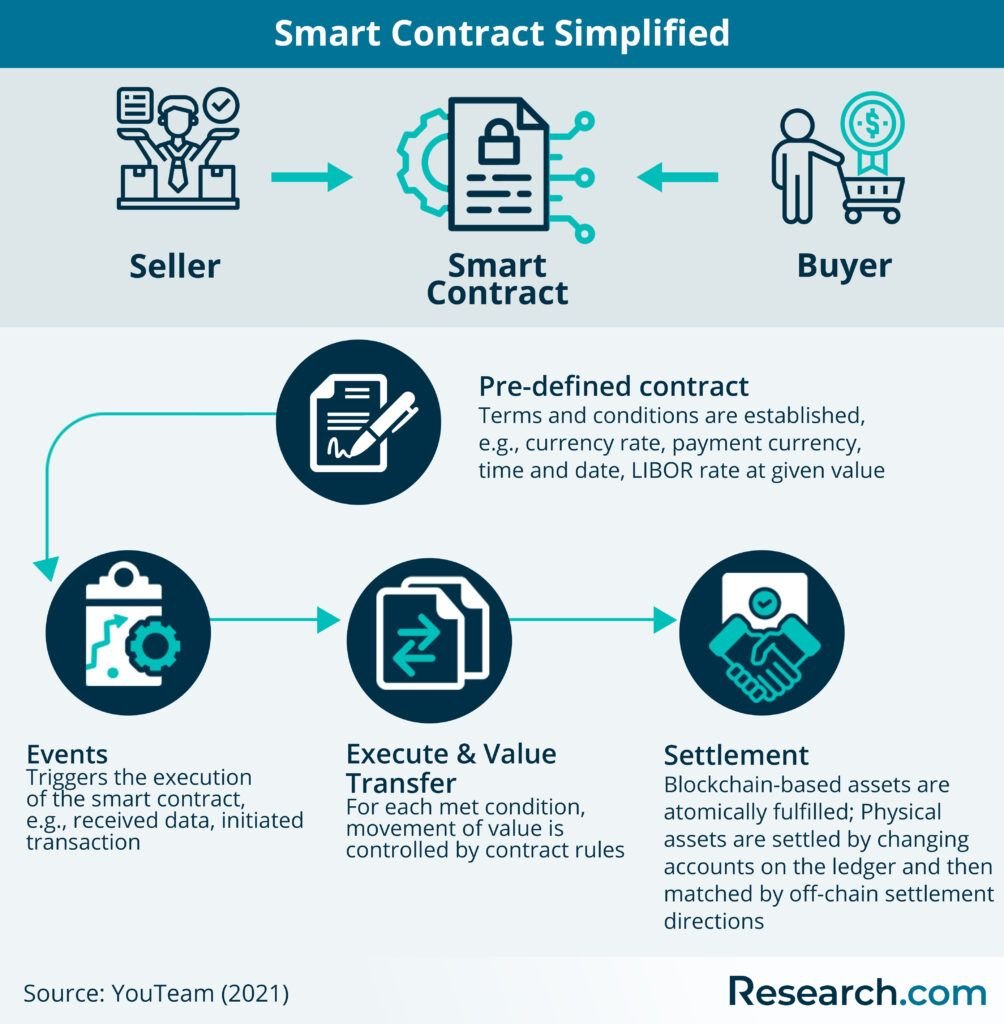
Smart contracts are digital agreements that are self-executing and enforceable by code. They are built on blockchain technology, which ensures transparency, security, and immutability. Understanding the basics of smart contracts is essential for anyone looking to leverage their benefits in legal agreements.
One key feature of smart contracts is their ability to automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces the risk of fraud, and increases the efficiency of contract management. Smart contracts can be used in various industries, including finance, real estate, supply chain, and more.
When creating a smart contract, parties define the terms and conditions of the agreement in code. Once deployed on the blockchain, the contract is immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or tampered with. This provides a high level of security and trust in the agreement, as all parties can verify the terms and track the execution of the contract.
Smart contracts use cryptographic technology to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the agreement. Each party involved in the contract has a unique cryptographic key that allows them to interact with the contract securely. This helps prevent unauthorized access and protects sensitive information shared within the agreement.
The benefits of using smart contracts in legal agreements
Smart contracts offer numerous advantages when it comes to legal agreements. One of the key benefits is their ability to automate and execute contracts without the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of errors or fraud. This automation also speeds up the process, saving time and resources for all parties involved.
Another advantage of using smart contracts is their transparency and immutability. Once a contract is deployed on a blockchain network, it cannot be altered or tampered with, providing a secure and trustworthy record of the agreement. This can help prevent disputes and ensure that all parties adhere to the terms of the contract.
Smart contracts also offer cost savings by eliminating the need for traditional legal services and reducing the administrative burden associated with contract management. This can be particularly beneficial for small businesses or individuals who may not have the resources to hire legal professionals.
Furthermore, smart contracts can help streamline complex agreements by automatically enforcing clauses and conditions based on predefined rules. This can reduce the likelihood of misunderstandings or misinterpretations, leading to smoother and more efficient contract execution.
Challenges and limitations of smart contracts in the legal industry
Smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize the legal industry by automating and streamlining contract processes. However, there are challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
- **Complexity**: Smart contracts can be complex to create and implement, requiring specialized technical knowledge. This complexity can be a barrier for legal professionals who may not have the necessary skills.
- **Security**: Security is a major concern with smart contracts, as they are vulnerable to hacking and other cyber threats. Ensuring the security of smart contracts is crucial to their success.
- **Enforceability**: One of the key challenges with smart contracts is their enforceability in a legal context. While smart contracts are designed to be self-executing, there may be legal issues that arise if a contract is breached.
- **Interoperability**: Smart contracts may not be compatible with existing legal systems and frameworks, making it difficult to integrate them into current practices. This lack of interoperability can hinder the adoption of smart contracts in the legal industry.
Despite these challenges, smart contracts have the potential to transform the legal industry by increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving transparency. By addressing these challenges and limitations, legal professionals can harness the power of smart contracts to revolutionize the way legal agreements are created and executed.
Real-world examples of smart contracts revolutionizing legal processes
Smart contracts have been revolutionizing legal processes across various industries. Here are some real-world examples showcasing how these digital agreements are transforming traditional legal agreements:
- Real Estate: Smart contracts are being used to streamline property transactions by automating the process of transferring ownership, verifying identities, and executing payments. This has significantly reduced the need for intermediaries and minimized the risk of fraud.
- Supply Chain Management: In the logistics industry, smart contracts are being utilized to track the movement of goods, automate payments based on delivery milestones, and enforce penalties for delays. This has improved transparency, efficiency, and trust among all parties involved.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Smart contracts are being employed to manage copyrights, patents, and trademarks by automatically enforcing licensing agreements, tracking royalties, and protecting digital content from unauthorized use. This has simplified the management of intellectual property rights and reduced disputes.
- Insurance: Smart contracts are transforming the insurance sector by automating claims processing, verifying policy conditions, and triggering payouts based on predefined criteria. This has expedited the settlement of claims, reduced administrative costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Employment Contracts: Smart contracts are reshaping the way employment agreements are executed by automating the onboarding process, managing payroll, and enforcing terms and conditions. This has increased compliance, reduced paperwork, and improved the overall employee experience.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and efficiency of smart contracts in revolutionizing legal processes across different sectors. As organizations continue to adopt this innovative technology, the potential for transforming traditional legal agreements into secure, transparent, and self-executing digital contracts is limitless.
Exploring the future of smart contracts in the legal sector
As we look ahead to the future of smart contracts in the legal sector, it is clear that these innovative digital agreements are poised to revolutionize the way legal transactions are conducted. Smart contracts have the potential to streamline processes, reduce costs, and increase efficiency in the legal industry.
One of the key advantages of smart contracts is their ability to automatically execute and enforce the terms of an agreement without the need for intermediaries. This not only speeds up the contract process but also reduces the risk of errors or disputes. By leveraging blockchain technology, smart contracts provide a secure and transparent way to conduct transactions.
Furthermore, smart contracts have the potential to expand access to legal services by making them more affordable and accessible. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals and small businesses who may not have the resources to engage in traditional legal agreements. By automating routine legal tasks, smart contracts can help level the playing field and empower a wider range of users.
Overall, the future of smart contracts in the legal sector looks promising. As technology continues to advance and regulations evolve to accommodate these digital agreements, we can expect to see a significant shift in the way legal agreements are created and enforced. By embracing smart contracts, the legal industry can adapt to the changing landscape and provide more efficient and cost-effective services to clients.
Key considerations when implementing smart contracts in legal agreements
Implementing smart contracts in legal agreements requires careful consideration of various key factors to ensure their effectiveness and compliance with existing laws and regulations. Some of the key considerations to keep in mind include:
- **Code Accuracy:** Ensuring that the smart contract code is accurate and free of errors is crucial to prevent any unintended consequences or disputes. Conducting thorough testing and audits can help identify and rectify any potential issues before deployment.
- **Legal Compliance:** Smart contracts must comply with relevant legal frameworks and regulations to be enforceable. It is essential to work closely with legal experts to ensure that the terms and conditions of the smart contract align with the law.
- **Security Measures:** Implementing robust security measures is vital to protect the smart contract from vulnerabilities and cyber threats. Utilizing encryption, multi-signature requirements, and secure key management practices can help enhance the security of the contract.
- **Dispute Resolution:** Establishing mechanisms for dispute resolution within the smart contract can help parties resolve conflicts efficiently. Including arbitration or mediation clauses can provide a framework for addressing disputes that may arise during the contract execution.
- **Data Privacy:** Smart contracts often involve the processing of personal data, so it is essential to consider data privacy regulations such as GDPR. Implementing data protection measures and obtaining consent from data subjects can help ensure compliance with privacy laws.
By carefully considering these key factors when implementing smart contracts in legal agreements, businesses can leverage the benefits of this innovative technology while mitigating potential risks and ensuring legal compliance. It is essential to seek guidance from legal and technical experts to navigate the complexities of smart contract implementation successfully.



